Clinical hand washing, also known as medical hand hygiene, refers to a specific technique used by healthcare professionals to thoroughly clean their hands in a clinical or medical setting. It is a critical practice to prevent the spread of infections and maintain a safe environment for patients.
Clinical hand washing involves more than just a quick rinse with water and soap. It follows a specific protocol that ensures the effective removal of microorganisms, including bacteria and viruses, from the hands. The steps involved in clinical hand washing typically include:
- Wetting the hands: Begin by wetting the hands and wrists thoroughly with clean, running water. Ensure that the water has a desirable temperature.
- Applying soap: Dispense an adequate amount of antimicrobial soap into the palm of one hand. The soap should be chosen based on its effectiveness in killing or reducing the growth of microorganisms.
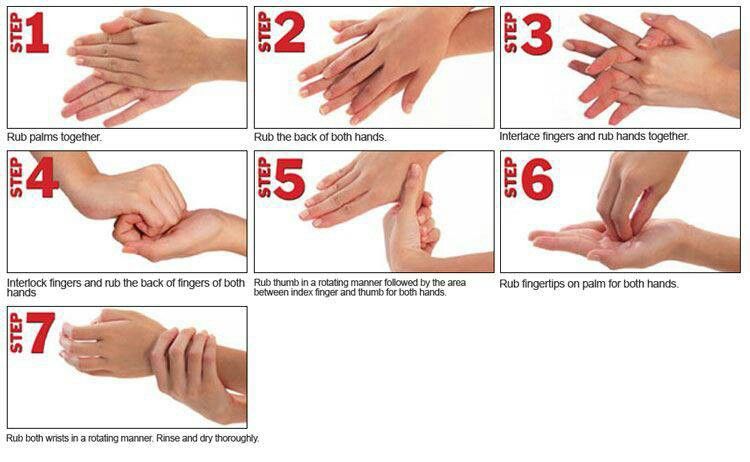
- Rubbing palms together: Rub the palms of your hands together vigorously in a circular motion. Ensure that the soap covers all surfaces of the hands, including the palms, back of the hands, fingers, and wrists. This action helps to create friction and dislodge any potential pathogens.
- Palm over dorsum: Place your right hand over the back of your left hand, interlacing your fingers, and then switch to put your left hand over the back of your right hand. Interlacing fingers: Hold your hands together by linking your fingers, with the backs of your fingers touching the palms of the other hand.
- Fingers interlace: Place your right hand on top of your left hand, interlacing your fingers, and then switch by placing your left hand on top of your right hand.
- Washing the thumbs: Grasp the thumb of one hand with the opposite hand and rub it in a rotational motion. Repeat the process for both thumbs.
- Cleaning the fingertips: Rub the fingertips of each hand against the opposite palm in a circular motion. This action helps to clean the tips and the areas underneath the nails.
- Cleaning the wrists: Pay attention to the wrists and clean them thoroughly. Microorganisms can accumulate in this area as well.
- Rinsing the hands: Rinse off the soap and any loosened debris under clean, running water.
- Drying the hands: Dry your hands using a clean, disposable towel or a hand dryer. Pat them dry thoroughly, starting from the wrists and moving towards the fingertips.
It is essential to note that clinical hand washing should be performed for a recommended duration of at least 20 seconds. This duration allows enough time for the soap to interact with microorganisms and effectively remove them from the hands.
Clinical hand washing is a vital practice that healthcare professionals follow to minimize the risk of transmitting infections from one patient to another. It is an integral part of infection control measures and plays a significant role in maintaining patient safety.
Importance of Clinical Hand Washing:
- Preventing Infections: Clinical hand washing plays a vital role in preventing the spread of infections in healthcare settings. Healthcare professionals come into contact with various types of pathogens on a daily basis, and proper hand hygiene can significantly reduce the transmission of harmful bacteria, viruses, and other microorganisms.
- Patient Safety: Hand washing is crucial for ensuring patient safety. Many patients in healthcare facilities have compromised immune systems or are recovering from surgeries, making them more susceptible to infections. By practicing proper hand hygiene, healthcare workers can minimize the risk of transferring pathogens from one patient to another, ultimately promoting better patient outcomes.
- Nosocomial infections, also known as healthcare-associated infections (HAIs), are infections that are acquired in a hospital or other healthcare facility. These infections develop as a result of exposure to infectious agents within the healthcare setting and can affect patients, healthcare workers, or visitors. They can make people stay in the hospital for a long time, make healthcare more expensive, and even cause death. Regular and thorough hand washing by healthcare professionals is one of the most effective measures for preventing HAIs, reducing their incidence and associated complications.
- Cross-Contamination Prevention: Clinical hand washing helps prevent cross-contamination, which occurs when pathogens are transferred from one surface to another. Healthcare workers may inadvertently touch contaminated surfaces, equipment, or patients, and without proper hand hygiene, they can unknowingly spread harmful microorganisms to other patients or areas within the healthcare setting.
- Compliance with Regulations and Guidelines: Hand hygiene is a fundamental aspect of infection control, and healthcare facilities are required to adhere to specific regulations and guidelines to maintain patient safety. By practicing clinical hand washing, healthcare professionals ensure compliance with these standards, reducing the risk of legal implications and ensuring a safe healthcare environment.
- Staff Health and Well-being: Hand washing not only protects patients but also promotes the health and well-being of healthcare professionals themselves. By regularly washing their hands, healthcare workers minimize their own risk of acquiring infections from patients, providing a safer working environment and preventing absenteeism due to illness.
- Public Health Impact: Clinical hand washing extends beyond healthcare settings. It is an essential practice that should be adopted by everyone to prevent the spread of infectious diseases in the community. By raising awareness about the importance of hand hygiene, healthcare professionals can influence public behaviour and contribute to overall public health.
In conclusion, clinical hand washing is of paramount importance in healthcare settings. It prevents infections, protects patients, reduces healthcare-associated infections, prevents cross-contamination, ensures compliance with regulations, promotes staff health, and has a positive impact on public health. Practicing proper hand hygiene is a simple yet powerful measure that significantly contributes to the overall well-being of individuals and the community.